As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, mergers and acquisitions (M&As) have become a strategic tool for providers to expand their reach, enhance services and improve efficiency. This year, certain states have emerged as particularly active hubs for healthcare services M&A. The healthcare services sectors included in this report include Behavioral Health Care, Home Health & Hospice, Hospitals, Laboratories, MRI & Dialysis, Long-Term Care, Managed Care, Physician Medical Groups, Rehabilitation and Other Services (a mix of companies providing ancillary healthcare services, or those relating to healthcare).
This analysis examines the most active U.S. states and regions for healthcare services M&A so far throughout 2024, highlighting the key factors influencing activity and the opportunities and challenges shaping the healthcare landscape.
Regional Breakdown Year to Date (As of August 19, 2024):
| Region | Deal Totals Per State |
| Northeast | This region is made up of nine states: Pennsylvania (29 deals), New York (30), New Jersey (30), Vermont (4), New Hampshire (4), Connecticut (11), Rhode Island (7), Massachusetts (20) and Maine (4) |
| Southwest | This region is made up of Texas (82 deals), Oklahoma (6), New Mexico (3) and Arizona (30) |
| West | The West region is made up of Colorado (22 deals), Idaho (8), Nevada (6), Utah (8), Wyoming (0), Montana (2), California (76), Oregon (6), Washington (13), Alaska (1) and Hawaii (2) |
| Southeast | This region includes Washington, D.C. (0 deals), Delaware (2), Maryland (15), West Virginia (3), Virginia (20), Kentucky (15), Tennessee (28), North Carolina (27), South Carolina (20), Georgia (28), Florida (93), Alabama (15), Mississippi (11), Arkansas (11) and Louisiana (9) |
| Midwest | This region consists of 12 states: Ohio (41 deals), Indiana (16), Illinois (24), Michigan (21), Wisconsin (18), Minnesota (13), North Dakota (2), South Dakota (1), Iowa (4), Kansas (3), Nebraska (3) and Missouri (15) |
Healthcare Services M&A Per State, Year to Date
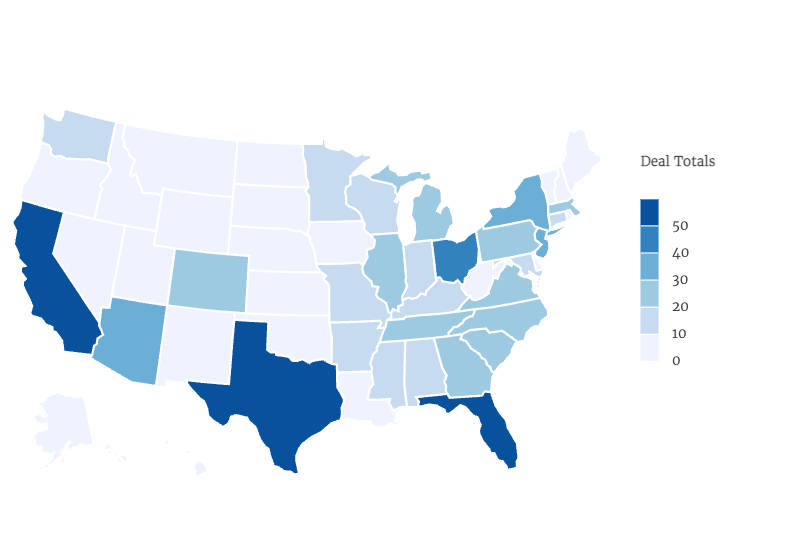
Source: LevinPro HC, January 1, 2024-August 19, 2024
M&A Activity by State and Region
Florida stands out as the most active state for healthcare services M&A, with 93 deals recorded year to date. This high number is driven by factors such as a large and growing population, increased demand for healthcare services and a recent relaxation of Certificate of Need (CON) laws, which we will explore in more detail later. Texas and California follow closely behind, with 82 and 76 deals, respectively, reinforcing their status as healthcare M&A powerhouses.
In the Northeast, M&A activity has been concentrated in Pennsylvania, New York and New Jersey. The Southeast, with its generally less restrictive regulatory environment, has also experienced robust dealmaking, particularly in Georgia, North Carolina and Tennessee.
The West has also been very active, heavily driven by its largest state, California, which recorded 76 deals. The region’s M&A activity is also being fueled by states such as Colorado, Arizona and Washington.
The Midwest presents a varied landscape. States like Ohio, Indiana and Illinois have experienced substantial dealmaking, while others, such as North Dakota and South Dakota, have seen fewer transactions.
The Impact of CON Laws
CON laws, requiring government approval for certain healthcare capital projects, have significantly influenced M&A activity across the country. States with more stringent CON regulations tend to experience lower deal volumes as these laws introduce bureaucratic hurdles and uncertainty. However, these laws are not insurmountable barriers. Some states have implemented more flexible CON processes and strategic partnerships can sometimes overcome these challenges.
As of 2023, approximately 35 states have some form of CON laws. States without CON programs, including California, Texas and Colorado, tend to see more robust M&A activity due to fewer regulatory hurdles. While this is generally true, the Northeast offers a notable exception. Despite stringent CON regulations in some states, the region has maintained a steady pace of M&A due to factors such as a dense population, urban centers, strong academic medical centers and a favorable payer mix. These factors have allowed healthcare providers in the Northeast to navigate the complexities of CON laws more effectively.
Florida’s recent relaxation of its CON laws exemplifies how regulatory changes can stimulate M&A activity. By removing bureaucratic obstacles, the state has created a more attractive environment for healthcare investors and providers.
While CON laws can slow down deal timelines and increase transaction costs, they do not necessarily prevent deals from happening altogether. Instead, they influence the volume, size and complexity of transactions. Understanding the specific nuances of CON regulations in different states is crucial for assessing the M&A landscape.
Other Factors Influencing M&A
Beyond CON laws, several other factors contribute to the variability in M&A activity across states. Market size, healthcare spending, population growth and state policies all play critical roles. For example, states with larger populations and higher healthcare spending, such as Florida and Texas, naturally see more M&A activity. This is also true for California, which has become a hotbed for healthcare deals. Conversely, states with smaller populations and lower healthcare spending, such as Wyoming or Vermont, may experience fewer M&A transactions.
Demographic shifts, particularly the aging population, can be a driver of healthcare M&A activity in some states. States with a higher proportion of elderly residents are experiencing increased demand for services, driving M&A activity among providers seeking to capitalize on this growing market. Florida and Arizona, for instance, have emerged as hotspots due to their sizable retiree populations.
State policies can also significantly impact M&A activity. States with favorable tax incentives for healthcare businesses may attract more investment and M&A interest. For example, some states, like Delaware, Texas and Georgia, offer tax breaks for healthcare investments or research and development activities. Additionally, other states with supportive regulations for telehealth or value-based care models, like Colorado, Oregon and Maryland, can foster innovation and create opportunities for partnerships and acquisitions.
Another factor that can influence M&A is the mix of payers in a state, such as Medicare, Medicaid and commercial insurers. States with a higher proportion of commercial payers, such as California (54% of residents enrolled in commercial health plans), Texas (also 54%) and Colorado (58%) often have more profitable healthcare markets, attracting more M&A interest compared to states with a larger Medicaid population.
Additionally, reimbursement rates for healthcare services can impact a state’s attractiveness. For instance, states with higher Medicare reimbursement rates, such as those in the Northeast, often attract more healthcare providers and potential M&A targets.
The post-COVID-19 era has introduced new complexities to the M&A landscape. While the initial shock of the pandemic led to a slowdown in dealmaking, the subsequent economic recovery and government stimulus packages have fueled a resurgence in M&A activity. For example, New York, a major epicenter of the pandemic, received substantial federal aid, with $5.1 billion allocated to its Coronavirus relief fund. California, with the nation’s largest economy, was also significantly impacted by the pandemic and received funding as a result, including $15.3 billion from the CARES Act. The federal funding helped both states stabilize their economies, prevent mass layoffs and maintain consumer spending, making the post-pandemic bounce-back less harsh. However, other states, like Montana, received significantly less federal funding and have experienced a slower recovery in healthcare M&A, highlighting the disparate impact of the pandemic on different regions, even four years later.
However, the healthcare industry faces significant headwinds that could impact M&A activity in each state as well. Ongoing economic uncertainties, supply chain disruptions and labor shortages continue to pose challenges for healthcare organizations. And we’d be lying if we said we knew how the market will pan out after the coming election.
These factors are likely to influence deal valuations, transaction structures and overall M&A activity in the coming months, making it crucial for stakeholders to stay agile and informed as they navigate this evolving market. Understanding these dynamics will be key to identifying the states and regions poised for continued M&A growth in the years ahead.


